Surety Bonds
Surety bonds are a type of financial guarantee involving three parties: the principal, the obligee, and the surety.
Principal: The party that purchases the bond and is responsible for fulfilling a specific obligation (e.g., a contractor completing a project).
Obligee: The party that requires the bond and is protected by it (e.g., a government agency or a business).
Surety: The company that issues the bond and guarantees that the principal will fulfill their obligations. If the principal fails to do so, the surety covers the loss or damage.
The bond essentially ensures that if the principal does not meet their obligations, the obligee will be compensated for any resulting financial loss. The principal is then responsible for repaying the surety.
Surety bonds are commonly used in situations where a party wants to ensure the completion of a project, compliance with regulations, or the protection against fraud, theft, or other financial risks. Examples include contractor bonds, license bonds, court bonds, and vehicle title bonds.
There are several common types of surety bonds, each serving different purposes. Some of the most frequently encountered include:
Contractor Bonds (Performance and Payment Bonds):
Performance Bonds: Ensure a contractor will complete a project according to the terms of the contract.
Payment Bonds: Guarantee that contractors will pay subcontractors, laborers, and suppliers.
License and Permit Bonds:
Required by local, state, or federal authorities to ensure businesses comply with laws and regulations. Examples include bonds for contractors, auto dealers, and other licensed professionals.
Court Bonds:
Appeal Bonds: Used when a party appeals a court decision, ensuring that the appealing party will cover any costs or judgments if they lose the appeal.
Fiduciary Bonds: Used by individuals managing the finances of another person, like in guardianships or estates.
Bail Bonds: Guarantees that a person will appear in court if released on bail.
Fidelity Bonds:
Protects businesses against employee dishonesty, such as theft or fraud.
Customs Bonds:
Ensures compliance with regulations for importing goods, paying duties, and handling other customs-related obligations.
Notary Bonds:
Required for notaries to protect against mistakes or misconduct in their official duties.
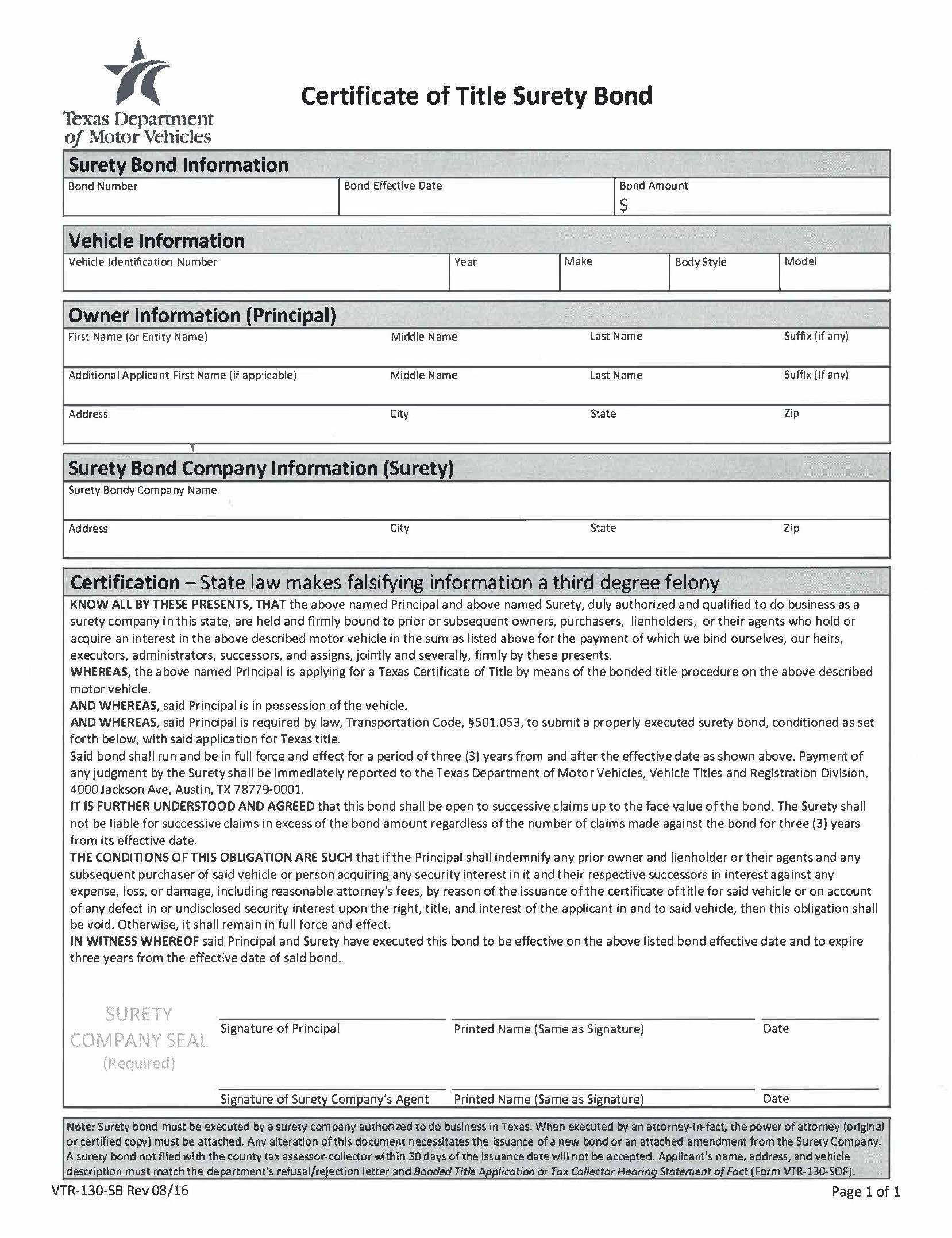
Vehicle Title Bonds:
Used when someone needs to obtain a title for a vehicle without proper documentation (e.g., lost or missing title).
These bonds help protect the public, ensure compliance, and provide financial security in various business and legal activities.